Video channel
Video channel
The Reuse Company
SES ENGINEERING Studio
-

Data Dictionaries - the springboard towards high-quality system requirements
-

How to deal with changes in PDF regulation for System Engineers
-

Unlocking Cross Platform Potential - A Deep Dive into Systems Engineering Interoperability
-

Collaboration in MS Word - Change Management
-

Propagating changes from traceability links
-

Carrying your requirements everywhere
-

Core domains of The REUSE Company
-

SES ENGINEERING Studio - CF
-

Technical Management Support in SES ENGINEERING Studio
-

Connectivity in SES ENGINEERING Studio
-

Managing traceability in MS Word
-

Managing requirement baselines and versions in MS Word
-

Writing high quality requirements in MS Word
-

Managing requirement attributes in MS Word
-

Parsing existing MS Word documents using different techniques
-

Boosting MS Word with Requirements Management Capabilities - Introduction
-

System Life Cycle Management with SES ENGINEERING Studio
-

Systems Engineering Rigor needs an Interoperability Framework
-

Interoperability in SES ENGINEERING Studio
-

Controlling the values of your signals in technical specifications
-

Configuration Management with SES ENGINEERING Studio
-

Requirements Management through AIIG contracts
-

Connecting the Dots: Interoperability between your favourite Systems Engineering tools
-

Requirements Management: Managing data over entire life cycles
-

Taming the SE Life Cycle using Connectivity and Interoperability: the SES ENGINEERING Studio
RQA - QUALITY Studio
-

Passive voice requirements: Why ”passive voice” actually can become a nightmare
-

SES ENGINEERING Studio for Requirements
-

Raise the ante: high-quality models is the only way forward after high-quality requirements
-

How to generate a quality report of your requirements based on the INCOSE Guidelines
-

Why Challenging the INCOSE Consistency metrics might benefit your requirements
-

Completeness: tips and tricks for high-quality specifications
-

Improve the quality of your requirements using advanced Correctness metrics in RQA - QUALITY Studio
-
![Capturing content for your knowledge base with KM, RQA and RAT [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/olysDbzwxCs/sddefault.jpg)
Capturing content for your knowledge base with KM, RQA and RAT [Webinar]
-
![Requirements patterns for Requirements Quality Analysis and Requirements Writing [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/EeF4VZ0AoiI/sddefault.jpg)
Requirements patterns for Requirements Quality Analysis and Requirements Writing [Webinar]
-
![Advanced requirements verification using parameterized metrics in RQA [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Wuvo5jcp-Mk/sddefault.jpg)
Advanced requirements verification using parameterized metrics in RQA [Webinar]
-
![How to check requirements consistency with RQA and IBM DOORS [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/lg9KmuLGOjE/sddefault.jpg)
How to check requirements consistency with RQA and IBM DOORS [Webinar]
-
![Checking requirements completeness with RQA and IBM DOORS [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/5oPe_IzJRYY/hqdefault.jpg)
Checking requirements completeness with RQA and IBM DOORS [Webinar]
-
![Requirements Quality along the Supply Chain [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/6mgPZ_e1MF4/sddefault.jpg)
Requirements Quality along the Supply Chain [Webinar]
-

Requirements Quality with Logical & Physical models (Rhapsody & Simulink) and Ontologies (Protégé)
-
![First steps to improve the quality of your requirements [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/OzcsbBuHRQk/sddefault.jpg)
First steps to improve the quality of your requirements [Webinar]
-

How to write requirements in the Space Industry using a Knowledge Library based on ECSS Standards
-
![Applying Machine Learning Techniques to the Flexible Assessment of Requirements Quality [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aB0tnT36UaI/sddefault.jpg)
Applying Machine Learning Techniques to the Flexible Assessment of Requirements Quality [Webinar]
-
![Getting Started with Requirements Quality Assessment [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ayRRBq4i0yk/sddefault.jpg)
Getting Started with Requirements Quality Assessment [Webinar]
-
![INCOSE Guide for Writing Requirements: real-time quality assessment of the INCOSE rules [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/UhYv2-x1CoQ/sddefault.jpg)
INCOSE Guide for Writing Requirements: real-time quality assessment of the INCOSE rules [Webinar]
-

Writing Requirements with a Knowledge Library Based on the NASA Systems Engineering Handbook
-

ECSS Drafting Rules: the best way to write standards and other documents based on the ESA rules
-
![Real-time quality assessment tailoring the INCOSE Guide for Writing Requirements [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TFHFoGR3rFM/sddefault.jpg)
Real-time quality assessment tailoring the INCOSE Guide for Writing Requirements [Webinar]
-
![Enhance the quality of your requirements specifications with RQA and DOORS [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/mn13a3WU2yU/sddefault.jpg)
Enhance the quality of your requirements specifications with RQA and DOORS [Webinar]
-
![Managing requirement quality with PTC Integrity Lifecycle Manager and Integrity Modeler [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/3G2VYnaCj3w/sddefault.jpg)
Managing requirement quality with PTC Integrity Lifecycle Manager and Integrity Modeler [Webinar]
-

RQA and RAT Railway demo
RAT - AUTHORING Tool
-

Correctness in Teamcenter
-
Pattern Assist in Teamcenter
-

Quality assessment in Teamcenter
-

RAT for Capella - Use Case 4
-

RAT for Capella - Use Case 3
-

RAT for Capella - Use Case 2
-

RAT for Capella - Use Case 1
-

Ensuring requirements quality with the MASTER patterns by Sophist and RAT - Authoring Tools [Webinar
-

RAT Integration on PTC Integrity
-
![Managing the quality ecosystem: DOORS, Rhapsody, Simulink and Modelica [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Jze54IMlrsk/sddefault.jpg)
Managing the quality ecosystem: DOORS, Rhapsody, Simulink and Modelica [Webinar]
-

Requirements Manager R2019x - Integration with Quality Assessment
-
![Writing perfect textual requirements in Capella MBSE Tool [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/eUzQYqP7ZDc/hqdefault.jpg)
Writing perfect textual requirements in Capella MBSE Tool [Webinar]
-

Writing perfect textual requirements in Capella MBSE Tool | The REUSE Company | Capella Webinar
-
![RAT – Authoring Tools: a widget for IBM DOORS NG to strengthen requirements authors [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/s5K5LXspJ8w/sddefault.jpg)
RAT – Authoring Tools: a widget for IBM DOORS NG to strengthen requirements authors [Webinar]
-
![RAT for Capella – The perfect way for working with both Models and Textual Requirements [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/O6lql1R-vaw/sddefault.jpg)
RAT for Capella – The perfect way for working with both Models and Textual Requirements [Webinar]
-

RQA and RAT Railway demo
KM - KNOWLEDGE Manager
-

How to kick off your KM KNOWLEDGE Management project
-

Automatically Verifying the Quality for Professional Requirements according to the BABOK® Guide
-

Knowledge Management Process: Using patterns to improve systems engineering projects
-
Knowledge Management Process: Organizing your ontology
-

IW2022 Ontologies Usage in Requirements Ilyes Yousfi
-
How to import a Library with KM - Knowledge Manager
-
![Capturing content for your knowledge base with KM, RQA and RAT [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/olysDbzwxCs/sddefault.jpg)
Capturing content for your knowledge base with KM, RQA and RAT [Webinar]
-
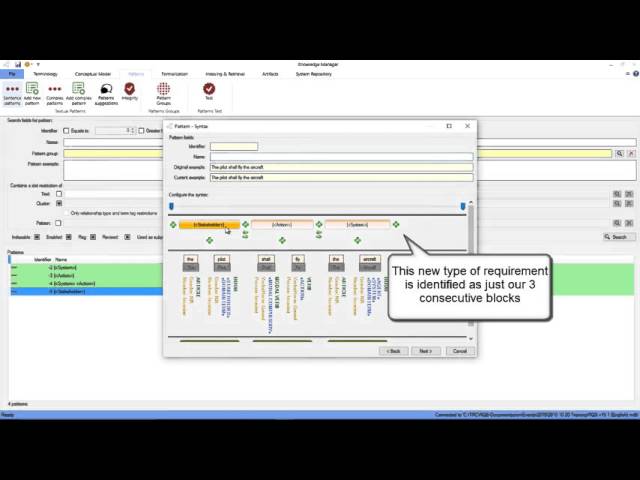
Knowledge Manager. Creation of requirements patterns
TRACEABILITY Studio
-

Semantic traceability: how to keep the digital thread all along the Systems Engineering lifecycle
-

TRACEABILITY Studio: a SMART tool to automatize the management of traces
-
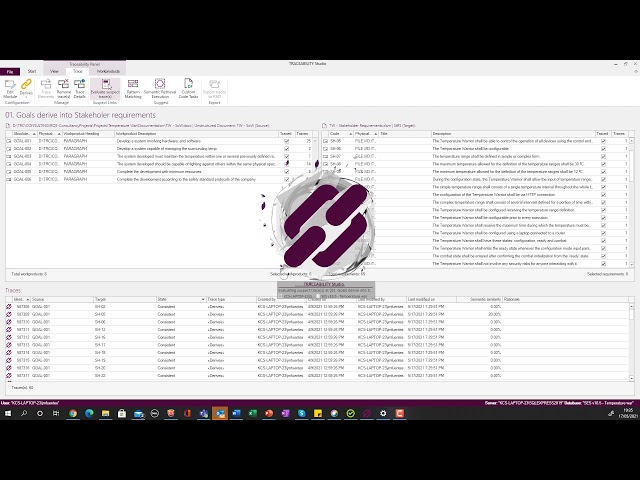
TRACEABILITY Studio: managing suspect links with a semantic tool
-

TRACEABILITY Studio: suggestion of new traces with a semantic tool
-

TRACEABILITY Studio Demo
-
![Automatic Traceability Discovery for Systems Engineering [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/U2S42Ly9EDI/sddefault.jpg)
Automatic Traceability Discovery for Systems Engineering [Webinar]
-
![SMART Traceability - the core of a successful systems engineering discipline [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/WQAslzsYDV8/sddefault.jpg)
SMART Traceability - the core of a successful systems engineering discipline [Webinar]
V&V Studio
-
Digitalizing the V&V process on both sides of the V Model
-

V&V Studio - SoW Verification
-

V&V Studio - Custom Code Verification
-

V&V Studio - Budget Verification
-

V&V Webinar demo
-

V&V Studio: 7 - Full Demo
-

V&V Studio: 6 Status Evolution Dashboard
-

V&V Studio: 5 - Interoperability
-

V&V Studio: 4 - Manual Video And File
-

V&V Studio: 3 - Quality
-

V&V Studio: 2 - Checklist
-
V&V Studio: 1 - Templates
-

V&V Studio Executing FMU
-

V&V Demo Custom Excel
-
![A Practical Way to Implement ISO 15288 V&V Processes: The V&V Studio [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/m1UirkOY798/sddefault.jpg)
A Practical Way to Implement ISO 15288 V&V Processes: The V&V Studio [Webinar]
-
![Implementing ISO 15288 V&V Processes using the V&V Studio [Webinar]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ZvsFYKE5Fbg/sddefault.jpg)
Implementing ISO 15288 V&V Processes using the V&V Studio [Webinar]
Webinars
-

Unlocking Cross Platform Potential - A Deep Dive into Systems Engineering Interoperability
-

Collaboration in MS Word - Change Management
-

Propagating changes from traceability links
-

Carrying your requirements everywhere
-

Managing Data for Acquisition
-

Managing traceability in MS Word
-

Managing requirement baselines and versions in MS Word
-

Writing high quality requirements in MS Word
-

Managing requirement attributes in MS Word
-

Parsing existing MS Word documents using different techniques
-

Boosting MS Word with Requirements Management Capabilities - Introduction
-

Systems Engineering Rigor needs an Interoperability Framework
-

Controlling the values of your signals in technical specifications
-

Configuration Management with SES ENGINEERING Studio
-

How to generate a quality report of your requirements based on the INCOSE Guidelines
-

Taming the SE Life Cycle using Connectivity and Interoperability: the SES ENGINEERING Studio
-

Requirements Management through AIIG contracts
-

Connecting the Dots: Interoperability between your favourite Systems Engineering tools
-

Semantic traceability: how to keep the digital thread all along the Systems Engineering lifecycle
-

Passive voice requirements: Why ”passive voice” actually can become a nightmare
-

Requirements Management: Managing data over entire life cycles
-

How to kick off your KM KNOWLEDGE Management project
-

Raise the ante: high-quality models is the only way forward after high-quality requirements
-

Digitalizing the V&V process on both sides of the V Model
-

Automatically Verifying the Quality for Professional Requirements according to the BABOK® Guide
-

Knowledge Management Process: Using patterns to improve systems engineering projects
-

Knowledge Management Process: Organizing your ontology
-

Reusing the knowledge existing in your models to improve requirements quality assessment
-

Knowledge Discovery Process: Automatic extraction of vocabulary from legacy documentation
-

Writing rules for numbers in textual requirements
Training SE Suite
-

How to import a Library with KM - Knowledge Manager
-

How to install the SE Suite
-

Terminology Completeness Coverage Metric
-

SCM Completeness Coverage Metric
-
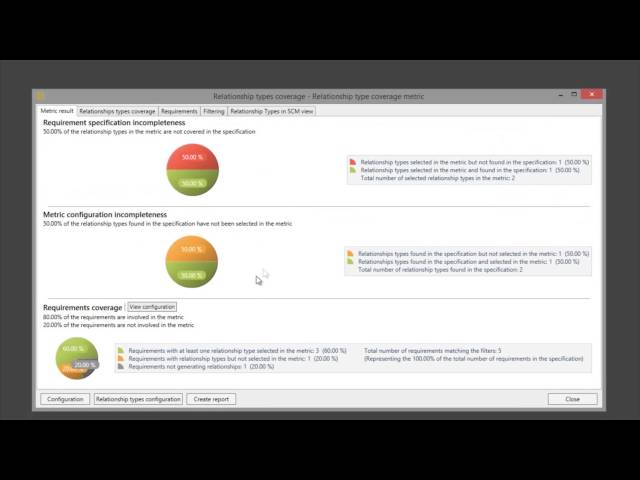
Relationship Types Completeness Coverage Metric
-

Model - Content Completeness Coverage Metric
-

Properties Completeness Coverage Metric
-

Patterns Completeness Coverage Metric
-

Links Completeness Coverage Metric
-
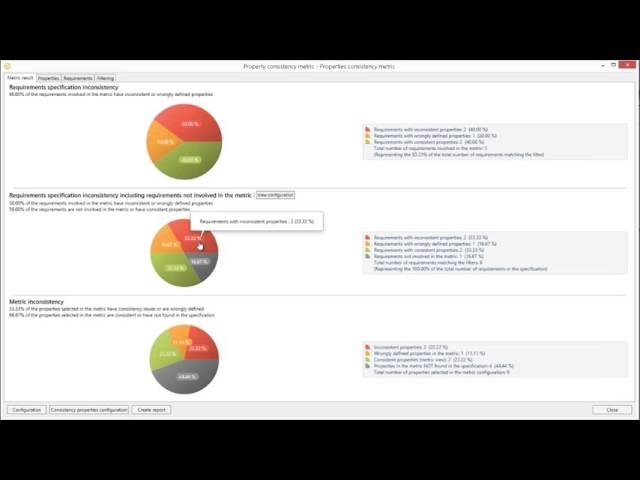
Property Values Consistency Metric
-
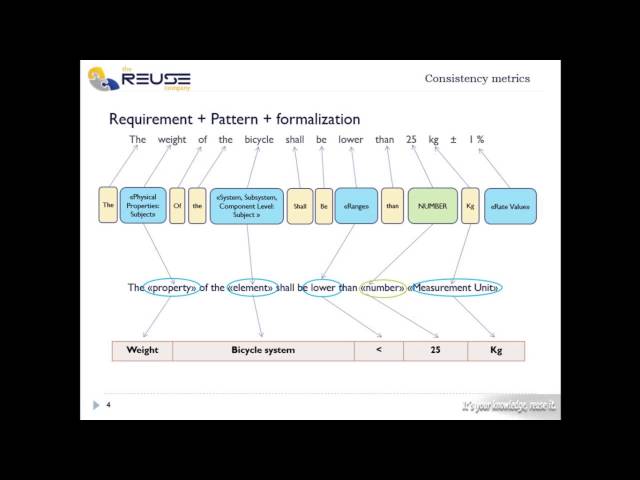
Arithmetic Operation Compliance Completeness Metric
-

Overlapping Requirements Consistency Metric
-

Measurement Units Consistency Metric
-
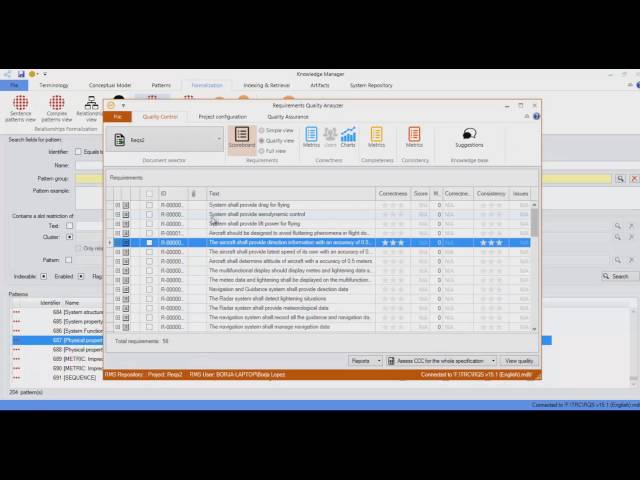
Measurement Units Consistency for specific property Metric
-

How to write high-quality requirements 1
-

How to write high-quality requirements 2
SE Suite in other languages
-

WEBINAR De cero a héroe: La Guerra de Temperatura. Un caso de uso acerca de Ingeniería de Sistemas.
-
RQA et RAT en Français.
-

Webinar in French: Introduction à l’analyse de qualité des exigences
-
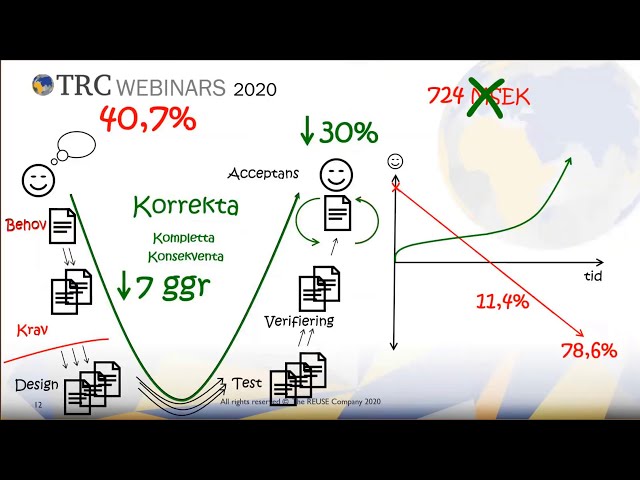
Webinar in Swedish: Kom igång med högkvalitativ kravgranskning för effektivare projektarbete
-

Webinar in German: Erste Schritte Richtung hochqualitative Anforderungen und erfolgreiche Projekte
-

Spanish webinar: Primeros pasos hacia requisitos de alta calidad y su impacto en el ahorro de costes
-

RQS demonstration in Italian from ASTER Systems Engineering Forum
Newsletter
Subscribe to our Newsletter