KM - KNOWLEDGE Manager
A SMARTer way to digitalize your knowledge

Knowledge management
Knowledge is one of the most valuable assets in an organization. The key to success in any system or software project is the reuse of knowledge assets. These include engineers’ explicit and tacit knowledge and guidelines defining organizational know-how.
Knowledge should therefore be gathered from different sources, stored in a secure repository, and accessed by the appointed person at the appropriate time.
KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager allows you to manage knowledge from a systems engineering point of view. You can also store valuable information from requirements, models, system architectures, and other documents in a System Knowledge Data Base.

Benefits of KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager
The more knowledge you store in a Knowledge Base, the more advanced engineering activities can be performed. Some of the benefits are:
Quality
Automatic verification of work products, semantic search engines along a project, semantic suggestion of traces, etc. will improve the quality of the project.
Time
KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager saves time as knowledge sharing and reuse activities among engineering tools become easier, allowing users to evolve and update ontologies seamlessly.
Money
Proper knowledge management is an asset for the organization. Better quality of the project and shorter time to market translate into savings and earnings.
Features of KM - KNOWLEDGE Manager
KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager is the tool you use to build and manage the information to be used in the rest of our tools.
Authoritative Source of Truth
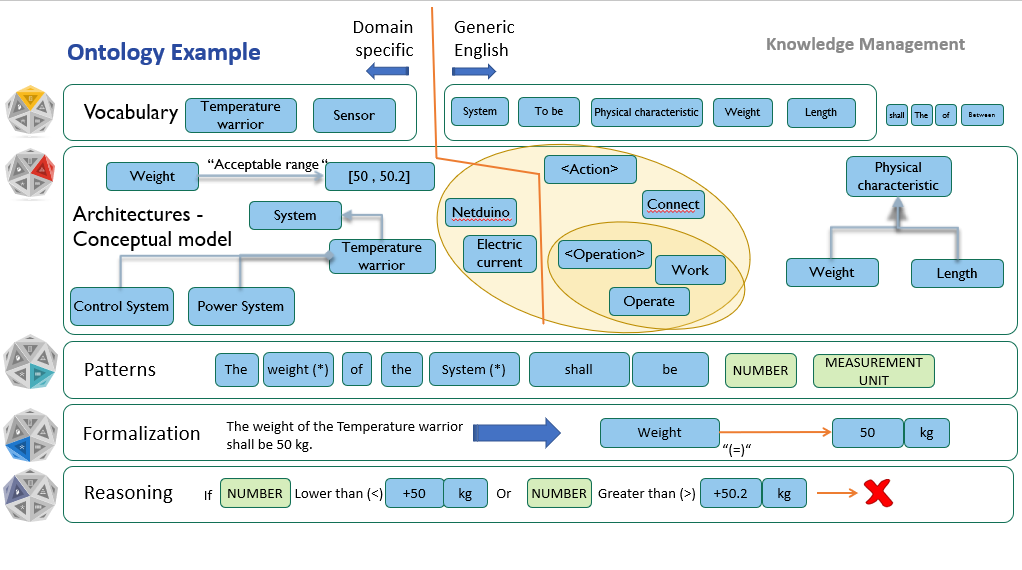
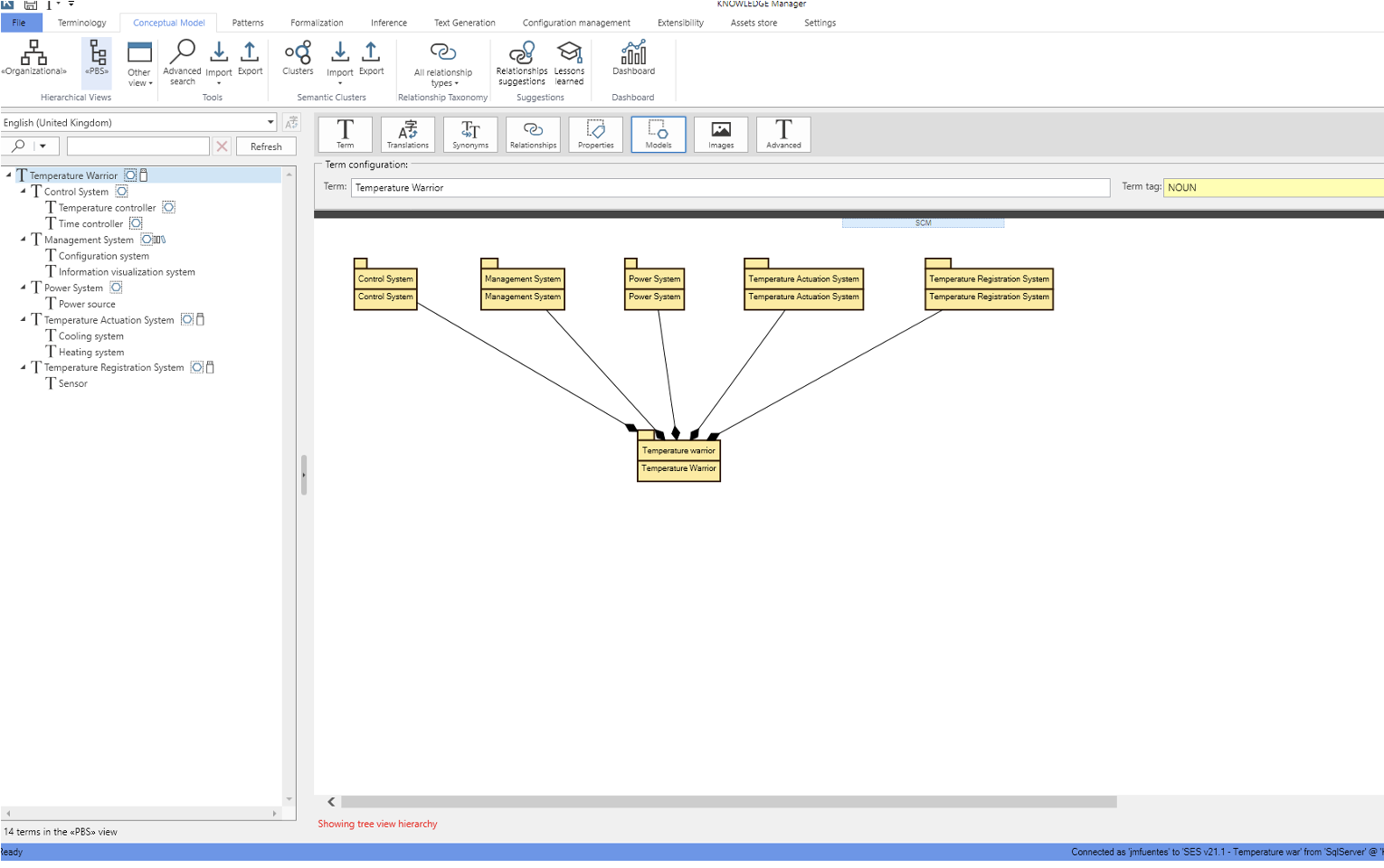
KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager permits the creation of a specific ontology to address the full complexity of the project’s context and tackle any kind of semantic structure required.
A controlled vocabulary is a must to facilitate consistency across the different work products developed during the life cycle of a project.
Ontologies in KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager help specific relationships between terms to fully represent a project’s context: synonyms, parent-child dependencies, subsystems, functional structures, etc.
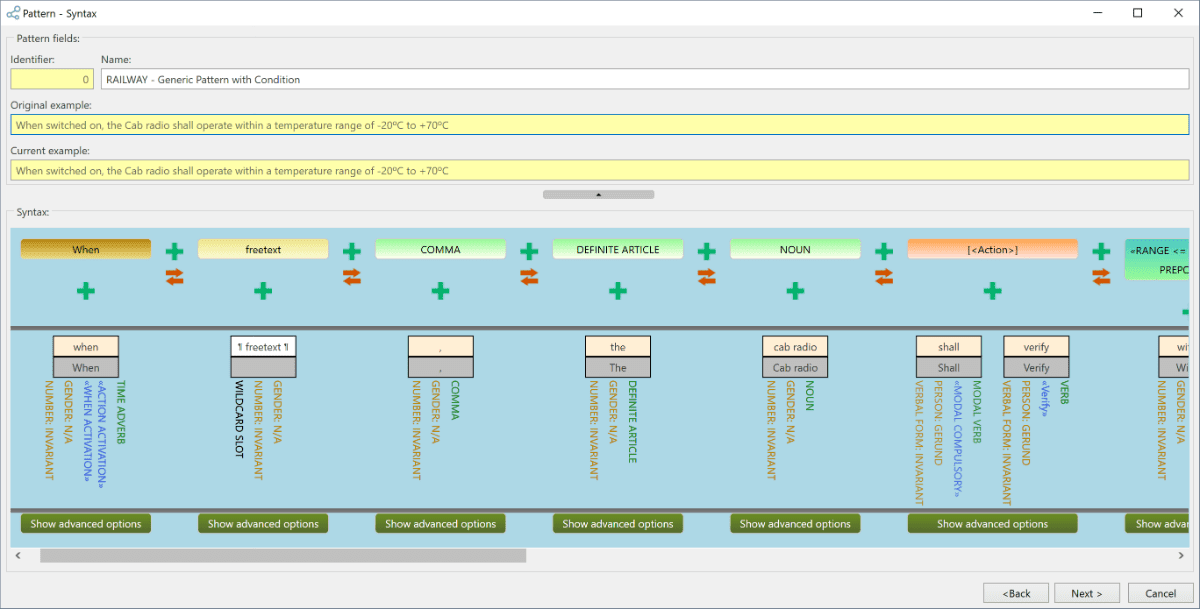
Patterns
The feature of creating textual patterns is a flexible solution to satisfy personalized preferences while writing requirements or other kinds of texts (risks, test scenarios, etc.). It helps optimize the editing process, standardize the writing approach, and englobe any possible variations within the requirements specifications.
External interfaces to build the ontology
The information of a project is usually stored in several formats (e.g. SysML/ UML models, requirements, simulations, tables, external databases, …). KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager is capable of connecting with several external sources to integrate this information inside the ontology.
Managing Knowledge Repositories
KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager is designed to manage all the knowledge needed for your system or software-intensive projects (breakdown structures, terms, acronyms, restrictions, etc.). Knowledge is stored within a System Knowledge Repository (SKR) and is organized in ontologies (called System Knowledge Base – SKB) and knowledge libraries. The Ontology and the libraries are used by the KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager for quality analysis, requirements, and textual work product authoring, to identify different types of link traces, transforming from requirements to models or test cases, identification of reusable products, etc.
KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager enables the management of the System Knowledge Repository, its System Knowledge Base, and all assets involved in the life cycle of your systems.
Knowledge management and systems engineering
KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager is the core tool for the Knowledge-Centric Systems Engineering approach. This approach takes advantage of all the knowledge developed during the system definition phase and makes it available to subsequent projects.
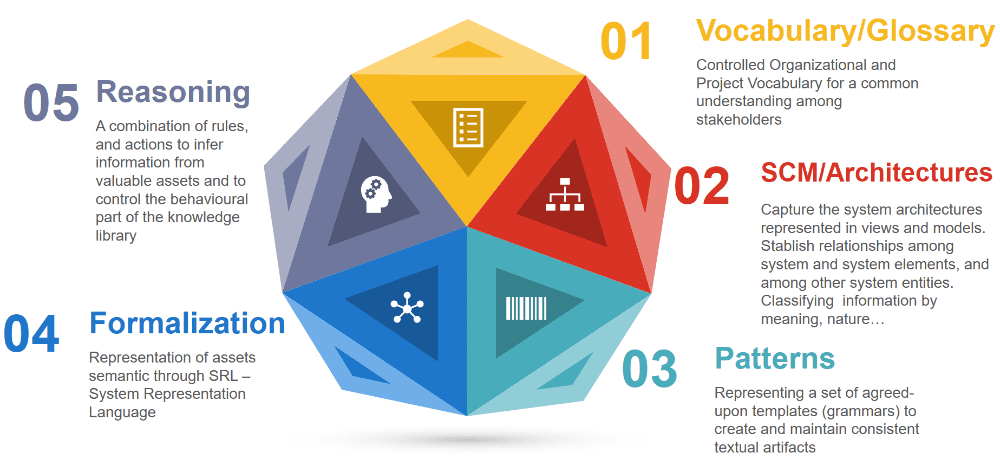
Our knowledge bases include 5 different layers:
- Fill your ontology with the domain-specific controlled vocabulary with the already included generic vocabulary.
- Create hierarchical structures and relationships between the terms of your controlled vocabulary to classify the new vocabulary. Then group concepts together within our semantic clusters to provide more semantics on top of the vocabulary.
- Design the textual structures and patterns you can reuse while writing requirements or other textual work products. The patterns can also be used in plenty of other semantic activities such as the identification of properties from textual sources, the suggestion of traces, etc.
- Once a pattern is “matched” for a given textual input, this input can be formalized (transformed) into one or several semantic graphs. Those semantic graphs are the right input for the reasoning layer performed by the system.
- The reasoning layer represents a complete toolbox that enables the semantic operation to be performed with your work products. This includes automatic verification of the quality of your items, the suggestion of traces, the semantic search engine, etc.
Textual patterns: standardize and rewrite requirements
Textual Patterns represent the grammatical structure a natural language sentence needs to follow according to an organization’s policies and know-how. Textual patterns can also be used to enable text transformation. By setting up source and target patterns for a transformation, the KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager will detect requirements that match the pattern and execute the transformation to the target structure while maintaining semantic consistency.
Semantic indexing and retrieval
KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager Uses Natural Language Processing tools and Artificial Intelligence algorithms. It provides a semantic search engine that enables the search and reuse of all sorts of information based on its actual meaning.
Libraries
KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager provides the capability to use knowledge libraries. These are combinations of knowledge items of different natures and levels of abstraction that can be reused in numerous projects. Knowledge management based on libraries is the best way to blend knowledge flexibly. At The REUSE Company, we provide a wide catalog of libraries ready to plug and play. Our current set of libraries is:
- INCOSE Knowledge Library: focuses on metrics defined as quality rules in the INCOSE Guide to Writing Requirements.
- EARS Knowledge Library: includes the catalog of patterns as defined in the Easy Approach to Requirements Syntax.
- SOPHIST Master Patterns Library: includes all the patterns described by SOPHIST in its Master Catalogue plus 18 rules for Requirements Writing.
- NASA Knowledge Library: includes the NASA Glossary plus the rules for writing requirements as described in the NASA Systems Engineering Handbook.
- ECSS Knowledge Library: includes terms, patterns, and drafting rules defined by the European Cooperation for Space Standardization.
- Requirements with Numbers Library: Including 17 metrics, dealing with the numbers used in textual requirements.
- BABOK® Library: Including a set of quality metrics covering the subsequent RADD characteristics and a set of patterns applied to cover the nine RADD characteristics.
External Connectors
External connectors allow merging between the knowledge natively managed in KM, and information coming from one or more external sources in real-time. Thus, if part of your knowledge is managed in MBSE tools, external ontologies in Protégé, or even MS Excel or Visio, there is no need to export and import in KM. You just add an external connector to KM – KNOWLEDGE Manager. When you use the Knowledge Base from other tools, like SES ENGINEERING Studio, the information from the external source will blend with the information from the KM ontology in real time.